Weather
Understanding Weather Forecasting
Introduction
Weather forecasting is a critical component of modern life, influencing everything from daily activities to global commerce. Accurate predictions of weather patterns allow individuals, businesses, and governments to plan effectively, minimizing risks associated with natural disasters and optimizing routine operations. In this article, we will delve into the science of weather forecasting, exploring the methods, tools, and technologies used to predict weather accurately.
The Science Behind Weather Forecasting
Weather forecasting is the process of predicting future atmospheric conditions based on the analysis of various meteorological data. This science relies on the understanding of several key factors, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. Meteorologists, or weather scientists, use this data to create models that simulate the Earth’s atmosphere and predict how it will behave in the future.
Types of Weather Forecasts
1. Short-Term Forecasting: This type of forecasting provides predictions for a period ranging from a few hours to a couple of days. Short-term forecasts are typically very accurate and are used for daily planning, such as determining whether to carry an umbrella or cancel outdoor events.
2. Medium-Term Forecasting: Medium-term forecasts cover a period of three to ten days. These forecasts are useful for planning vacations, business trips, or agricultural activities. While slightly less accurate than short-term forecasts, they still provide valuable insights into upcoming weather patterns.
3. Long-Term Forecasting: Long-term forecasts predict weather conditions over a period of weeks, months, or even seasons. These forecasts are crucial for industries such as agriculture and energy, which rely on long-term climate patterns for planning. However, they are less precise due to the complex nature of atmospheric dynamics.
Tools and Technologies in Weather Forecasting
The accuracy of weather forecasts has improved significantly over the past few decades, thanks to advancements in technology. Here are some of the key tools and technologies used in modern weather forecasting:
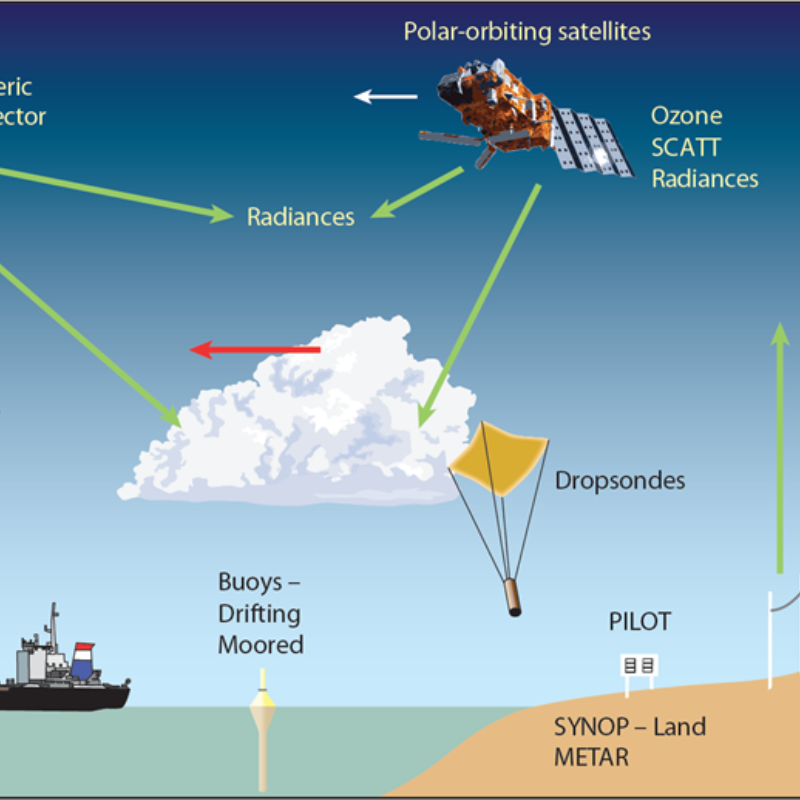
1. Satellites: Weather satellites orbit the Earth, providing real-time data on cloud cover, sea surface temperatures, and atmospheric moisture. This data is essential for monitoring large-scale weather systems such as hurricanes and typhoons.
2. Radar Systems: Weather radars detect precipitation, its intensity, and movement. This technology is particularly useful for tracking severe weather events like thunderstorms and tornadoes, allowing meteorologists to issue timely warnings.
3. Weather Stations: Ground-based weather stations collect data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. These stations are spread across the globe, providing localized weather data that is crucial for accurate forecasting.
4. Supercomputers: The vast amount of data collected by satellites, radars, and weather stations is processed by supercomputers. These machines run complex mathematical models that simulate the Earth’s atmosphere, allowing meteorologists to predict future weather patterns with greater accuracy.
5. Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models: NWP models are computer simulations of the atmosphere based on the laws of physics. These models use current weather data to predict future conditions. There are several types of NWP models, each with its strengths and weaknesses, and meteorologists often use a combination of models to improve accuracy.
Challenges in Weather Forecasting
Despite the advancements in technology, weather forecasting remains a challenging science. The Earth’s atmosphere is a chaotic system, meaning that small changes in initial conditions can lead to significant differences in outcomes. This phenomenon, known as the “butterfly effect,” makes long-term weather prediction particularly difficult.
Another challenge is the accuracy of data. While modern technology allows for the collection of vast amounts of meteorological data, there are still regions of the world, such as oceans and remote areas, where data collection is sparse. This lack of data can lead to less accurate forecasts in those regions.
Additionally, extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and flash floods, are inherently difficult to predict. While meteorologists can often forecast the general occurrence of these events, pinpointing their exact location, intensity, and timing remains a significant challenge.
The Role of Human Judgment
While technology plays a crucial role in weather forecasting, human judgment remains an essential component. Experienced meteorologists analyze the output of computer models, taking into account local knowledge, historical data, and current observations to refine predictions. This human element is particularly important when predicting severe weather, where small errors in timing or location can have significant consequences.
The Importance of Accurate Weather Forecasting
Accurate weather forecasting is vital for a wide range of activities and industries:
1. Public Safety: Timely weather forecasts allow governments to issue warnings and take preventive measures during extreme weather events, reducing the risk of injury and loss of life.
2. Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather forecasts to make decisions about planting, harvesting, and protecting crops from adverse weather conditions. Accurate forecasts can help maximize yields and reduce crop losses.
3. Transportation: Weather conditions have a significant impact on air, sea, and land transportation. Accurate forecasts help prevent accidents and delays, ensuring the safety and efficiency of travel.
4. Energy: The energy sector relies on weather forecasts to predict demand for heating and cooling. Renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, are also heavily dependent on weather conditions, making accurate forecasting essential for energy management.
5. Economy: Weather affects numerous aspects of the economy, from retail sales to construction. Businesses use weather forecasts to plan their operations, minimizing disruptions and maximizing profits.
Future Trends in Weather Forecasting
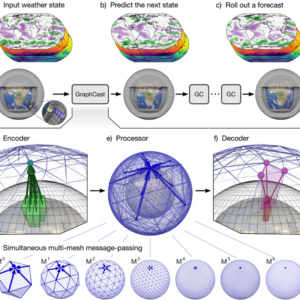
The future of weather forecasting looks promising, with continued advancements in technology expected to further improve accuracy. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are increasingly being used to analyze weather data, identify patterns, and make predictions. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize weather forecasting by providing more accurate and timely predictions.
Additionally, the deployment of new satellites and sensors will enhance data collection, particularly in remote and under-served regions. This will lead to better global coverage and more accurate forecasts.
Conclusion
Understanding weather forecasting is essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by the Earth’s ever-changing atmosphere. While predicting the weather will always involve some degree of uncertainty, advancements in technology and the expertise of meteorologists continue to improve the accuracy of forecasts. As we look to the future, the integration of AI, machine learning, and enhanced
Learn more: zgladnews