Weather
Seasonal Weather Trends
Weather plays a significant role in our daily lives, influencing everything from the clothes we wear to the activities we plan. Understanding seasonal weather trends is crucial for better planning, adapting to climate changes, and even for industries like agriculture and tourism. This article delves into the concept of seasonal weather trends, exploring their causes, effects, and how they have evolved over time.
What Are Seasonal Weather Trends?
Seasonal weather trends refer to the typical weather patterns that occur during specific seasons of the year. These patterns are influenced by various factors, including geographical location, altitude, proximity to large bodies of water, and prevailing wind patterns. For instance, winter in the Northern Hemisphere is typically characterized by cold temperatures, shorter days, and occasional snowfall, while summer brings warmer temperatures, longer days, and more sunshine.
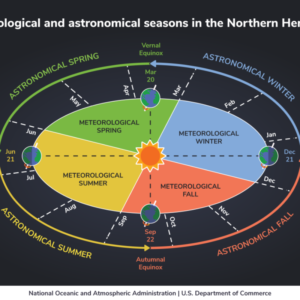
Factors Influencing Seasonal Weather Trends
1. Latitude: The Earth’s tilt and orbit around the sun are fundamental in determining the seasons. Regions closer to the equator experience less variation in temperature and daylight hours throughout the year, leading to more consistent weather patterns. Conversely, areas farther from the equator see more pronounced seasonal changes.
2. Ocean Currents: Ocean currents play a significant role in regulating weather patterns. Warm currents, like the Gulf Stream, bring warmer air and higher humidity to coastal areas, while cold currents can cool down regions and contribute to arid conditions. These currents can alter seasonal weather, leading to milder winters or cooler summers in certain areas.
3. Altitude: Higher altitudes generally result in cooler temperatures. Mountains can also block air masses, creating distinct weather patterns on their windward and leeward sides. For example, the windward side might experience heavy rainfall, while the leeward side stays dry.
4. Topography: The physical features of a region, such as mountains, valleys, and plains, significantly influence local weather patterns. For example, mountainous areas might experience cooler temperatures and more precipitation due to orographic lift, where moist air is forced to rise over mountains, cooling and condensing into clouds and precipitation.
5. Human Activity: Urbanization, deforestation, and other human activities have increasingly impacted weather patterns. Cities, for example, tend to be warmer than rural areas due to the urban heat island effect, where buildings and roads absorb and retain heat. Additionally, human-induced climate change is altering traditional seasonal patterns, making some regions warmer or cooler than they used to be.
Seasonal Weather Trends Across Different Regions
1. Tropical Regions: In tropical regions, near the equator, the seasonal variation is minimal, with temperatures remaining relatively constant throughout the year. However, these areas experience wet and dry seasons instead of the traditional four seasons. The wet season is typically characterized by heavy rainfall, while the dry season has less precipitation.
2. Temperate Regions: Temperate regions experience four distinct seasons—spring, summer, autumn, and winter. Each season brings its own weather patterns, with summer being warm, winter cold, and spring and autumn offering transitional weather. In these regions, the changing weather patterns are more pronounced, with significant differences in temperature and daylight hours between seasons.
3. Polar Regions: The polar regions experience extreme seasonal variations, with long, harsh winters and short, cool summers. During the winter months, these regions can go for weeks or even months without sunlight, known as polar night, while the summer months may bring continuous daylight, known as the midnight sun.
4. Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: These regions, including deserts, experience hot summers and mild winters with minimal precipitation. Seasonal weather trends in these areas are marked by extreme temperatures, with scorching hot days and cooler nights, particularly during the summer months.
Impact of Seasonal Weather Trends
1. Agriculture: Farmers rely on predictable seasonal weather patterns to plan planting and harvesting. Changes in these patterns can lead to droughts, floods, or unseasonal frosts, impacting crop yields and food security.
2. Tourism: Many tourist destinations are season-dependent. For instance, beach resorts thrive in the summer, while ski resorts rely on winter snowfall. Understanding weather trends helps the tourism industry prepare and market to potential visitors.
3. Health: Seasonal weather changes can influence public health. Cold winters can increase the risk of flu outbreaks, while hot summers can lead to heatwaves and related health issues. Awareness of these trends allows for better public health planning and response.
4. Energy Consumption: Seasonal weather trends directly impact energy usage. In colder seasons, heating demands rise, while in warmer seasons, air conditioning usage spikes. Understanding these patterns helps in planning energy resources and managing supply and demand.
The Changing Nature of Seasonal Weather Trends
In recent years, climate change has significantly impacted traditional seasonal weather patterns. Global warming is leading to hotter summers, milder winters, and more extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts. These changes are disrupting the usual weather patterns, making it more challenging to predict and prepare for seasonal changes.
For example, many regions are experiencing longer and hotter summers, with heatwaves becoming more common and intense. Winters, on the other hand, are becoming shorter and less severe in some areas, while others may experience unusually harsh winter storms. These changes are not only affecting the environment but also have profound implications for agriculture, wildlife, and human health.
Adapting to Changing Seasonal Weather Trends
As seasonal weather trends continue to evolve, adaptation becomes increasingly important. This includes:
1. Agricultural Adjustments: Farmers may need to change their planting schedules, select more resilient crops, or invest in irrigation and other technologies to cope with changing weather patterns.
2. Infrastructure Planning: Cities and communities must consider future weather trends in their infrastructure planning, such as flood defenses, heat-resistant buildings, and efficient energy systems.
3. Public Awareness and Preparedness: Public education campaigns can help people understand and prepare for changes in seasonal weather, such as stocking up on supplies before a harsh winter or taking precautions during a heatwave.

Conclusion
Seasonal weather trends are an essential aspect of life on Earth, influencing various sectors and daily activities. However, these patterns are not static and are increasingly being altered by climate change. Understanding and adapting to these changes is crucial for mitigating their impact and ensuring a sustainable future. Whether you’re a farmer, a city planner, or simply someone who enjoys outdoor activities, staying informed about seasonal weather trends can help you better prepare for the future.
Learn more: zgladnews


