Weather
Weather’s Impact in Agriculture
Agriculture is the backbone of many economies around the world, providing food, raw materials, and employment to billions of people. One of the most critical factors influencing agricultural productivity is weather. Weather’s Impact in Agriculture cannot be overstated, as it directly affects crop growth, soil health, pest control, and the overall success of farming operations. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which Weather’s Impact in Agriculture, the challenges it poses, and how farmers can mitigate the risks associated with weather variability.
Understanding Weather’s Impact on Crop Growth
Weather plays a fundamental role in determining the success of crop production. Key weather elements such as temperature, precipitation, sunlight, and wind are vital for the growth and development of crops.
1. Temperature: Temperature influences the rate of photosynthesis, respiration, and transpiration in plants. Different crops have specific temperature ranges in which they thrive. For instance, cool-season crops like wheat and barley prefer temperatures between 15°C to 20°C, while warm-season crops like maize and rice require temperatures between 25°C to 30°C. Extreme temperatures, either too hot or too cold, can hinder crop growth, reduce yields, or even cause crop failure.
2. Precipitation: Water is essential for plant growth, and precipitation is the primary source of water for crops. Adequate rainfall is necessary for maintaining soil moisture, which is crucial for seed germination, nutrient uptake, and photosynthesis. However, both excessive rainfall and drought can be detrimental. Flooding can lead to waterlogged soils, root rot, and nutrient leaching, while drought can cause water stress, reduced photosynthesis, and lower yields.
3. Sunlight: Sunlight is the energy source for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy to fuel their growth. The amount and intensity of sunlight affect the rate of photosynthesis, which in turn influences crop growth and yield. Cloudy or overcast conditions can reduce sunlight availability, slowing down photosynthesis and potentially leading to lower crop productivity.
4. Wind: Wind can have both positive and negative effects on agriculture. Gentle breezes can help with pollination and the dispersal of seeds, but strong winds can cause physical damage to crops, increase evaporation rates, and contribute to soil erosion. Additionally, wind can carry pests and diseases from one field to another, posing a threat to crop health.
Weather’s Impact Challenges in Agriculture
Weather variability and extreme weather events pose significant challenges to agriculture. Climate change has exacerbated these challenges, leading to more frequent and severe weather events that can disrupt farming operations and threaten food security.
1. Drought: Drought is one of the most severe weather-related challenges in agriculture. Prolonged periods of low rainfall can deplete soil moisture, reduce water availability for irrigation, and stress crops. Drought conditions can lead to lower yields, crop failure, and economic losses for farmers. In some regions, drought has become more frequent and intense due to climate change, making it increasingly difficult for farmers to sustain their livelihoods.
2. Flooding: On the other end of the spectrum, excessive rainfall and flooding can also have devastating effects on agriculture. Floodwaters can inundate fields, wash away topsoil, and damage crops. Waterlogged soils can lead to oxygen deprivation in plant roots, causing root rot and reduced nutrient uptake. Flooding can also delay planting and harvesting, disrupt supply chains, and lead to significant economic losses.
3. Heatwaves: Heatwaves, characterized by prolonged periods of excessively high temperatures, can cause heat stress in crops, leading to reduced growth, lower yields, and even crop failure. Heatwaves can also increase the rate of evaporation, leading to water shortages and further exacerbating the effects of drought. In recent years, heatwaves have become more frequent and intense, posing a growing threat to agriculture.
4. Frost: Frost occurs when temperatures drop below freezing, causing ice crystals to form on plants. Frost can damage or kill crops, especially if it occurs during critical growth stages such as flowering or fruiting. Frost events are more common in temperate regions, but they can also occur unexpectedly in warmer climates, catching farmers off guard and causing significant losses.
5. Pests and Diseases: Weather conditions can influence the prevalence and severity of pests and diseases in agriculture. For example, warm and humid conditions are conducive to the growth of fungal diseases, while dry and windy conditions can spread pests like aphids and locusts. Climate change has altered the distribution and behavior of many pests and diseases, making it more difficult for farmers to predict and manage these threats.
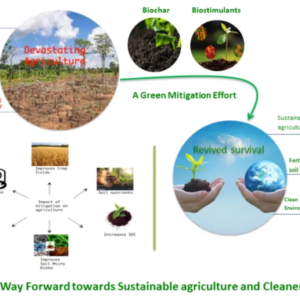
Stategies for Mitigating Weather Risks in Agriculture
Given the significant impact of weather on agriculture, farmers must adopt strategies to mitigate the risks associated with weather variability and extreme weather events. These strategies include:
1. Climate-Resilient Crops: Developing and planting climate-resilient crop varieties is one of the most effective ways to reduce the impact of adverse weather conditions. These crops are bred to withstand drought, heat, flooding, and pests, ensuring better yields even in challenging weather conditions. For example, drought-resistant maize varieties can thrive in regions with limited rainfall, while flood-tolerant rice varieties can survive in waterlogged fields.
2. Irrigation Management: Efficient irrigation systems are essential for managing water resources in agriculture, especially in regions prone to drought. Farmers can use drip irrigation, sprinkler systems, and soil moisture sensors to optimize water use and reduce water wastage. In areas with irregular rainfall, rainwater harvesting and storage can provide a valuable water source during dry periods.
3. Soil Conservation: Healthy soils are better able to retain moisture and nutrients, making them more resilient to weather extremes. Farmers can adopt soil conservation practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage to improve soil health and prevent erosion. Mulching and organic matter incorporation can also help maintain soil moisture levels during dry spells.
4. Weather Forecasting and Early Warning Systems: Access to accurate weather forecasts and early warning systems allows farmers to make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and irrigation. Governments and agricultural organizations can provide timely weather updates and alerts to help farmers prepare for adverse weather conditions and minimize potential losses.
5. Diversification: Diversifying crops and farming practices can reduce the risk of total crop failure due to adverse weather conditions. Farmers can plant a mix of crops with different weather sensitivities, ensuring that at least some crops will thrive regardless of the weather. Livestock farming, agroforestry, and integrated farming systems can also provide alternative income sources and enhance farm resilience.
Conclusion
Weather is an integral part of agriculture, influencing every aspect of crop production, from seed germination to harvest. While weather variability and extreme weather events pose significant challenges to farmers, adopting climate-resilient practices and technologies can help mitigate these risks. By understanding the role of weather in agriculture and implementing strategies to adapt to changing conditions, farmers can enhance their productivity, secure their livelihoods, and contribute to global food security. As the climate continues to change, the importance of weather in agriculture will only grow, making it essential for farmers, policymakers, and researchers to work together to build a resilient agricultural sector.
Learn more: zgladnews


